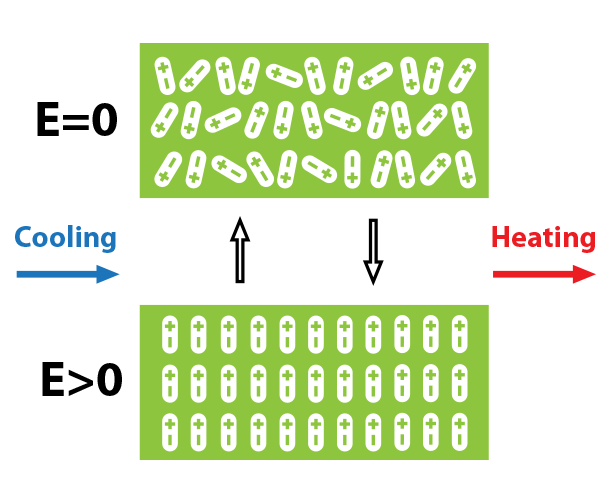
Electrocaloric Effect
When an electric field is applied to a dielectric material, it will induce a change in the polarization and, consequently, a change in the entropy and temperature in the material. Such an electric field induced temperature and entropy change in a dielectric material is known as the electrocaloric effect. The electrocaloric effect originates from the polar entropy change between an ordered and a disordered state. A dielectric material with a large number of polarization orientations and short polar-correlation, such as the relaxor ferroelectric, has the potential to achieve a large electrocaloric effect over a broad temperature range.
Electrocaloric Materials
- Polymers
- Ceramics
- Dielectric liquids
- Composites
Advantages of Electrocaloric Refrigeration
- More efficient than the conventional technologies
- No gases involved
- Low vibration and noise
- Compact size
- Light weight





